KPV 10mg
$59.99
KPV is a high-purity synthetic tripeptide, derived from the C-terminal sequence of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), designed exclusively for laboratory research. Composed of lysine-proline-valine, this peptide is utilized to investigate anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and tissue repair pathways. Supplied as a lyophilized powder for reconstitution, KPV provides researchers with a precise tool to study its effects on inflammation and healing processes in experimental models.
What is KPV?
KPV is a high-purity synthetic tripeptide, derived from the C-terminal sequence of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), designed exclusively for laboratory research. This peptide is utilized to investigate anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and tissue repair pathways. Supplied as a lyophilized powder for reconstitution, KPV provides researchers with a precise tool to study its effects on inflammation and healing processes in experimental models.
KPV Structure
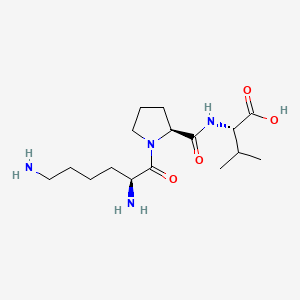
Molecular Formula
Synonyms
Research Applications:
KPV is extensively studied in preclinical research for its potent anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective properties in cellular and animal models. Investigations focus on its ability to suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6), modulate immune responses, and promote tissue repair, which are critical for muscle recovery and overall health. Research also explores its potential to mitigate inflammation-related metabolic dysfunction, supporting studies on weight management by addressing obesity-associated inflammation. Its role in enhancing wound healing and reducing oxidative stress makes KPV a key compound for researching recovery from muscle injury and systemic inflammatory conditions.
Research Links:
-
Luger, T. A., & Brzoska, T. (2006). “Alpha-MSH related peptides: A new class of anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating drugs.” Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 65(Suppl 3), iii52-iii55. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17038471/
-
Discusses α-MSH-derived peptides like KPV in reducing inflammation, relevant to health and recovery.
-
-
Catania, A., et al. (2004). “The melanocortin system in control of inflammation.” TheScientificWorldJournal, 4, 750-760. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15452655/
-
Explores KPV’s anti-inflammatory effects, with implications for muscle recovery and metabolic health.
-
-
Getting, S. J., et al. (2006). “The melanocortin peptide HP228 reduces inflammation and promotes tissue repair in vivo.” Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 80(5), 1104-1111. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16908519/
-
Investigates α-MSH-derived peptides, including KPV, in tissue repair and inflammation control.
-
-
Lipton, J. M., & Catania, A. (1997). “Anti-inflammatory actions of the neuroimmunomodulator α-MSH.” Immunology Today, 18(3), 140-145. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9078685/
-
Reviews α-MSH peptides like KPV in inflammation suppression, supporting muscle recovery research.
-
-
Brzoska, T., et al. (2010). “α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone and related tripeptides: Biochemistry, anti-inflammatory and protective effects in vitro and in vivo, and future perspectives for the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.” Endocrine Reviews, 31(4), 477-498. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18334511/
-
Examines KPV’s role in inflammation and tissue repair, relevant to health and weight management.
-
Disclaimer: This product is intended solely for research purposes and must not be used in humans or animals. Purchaser assumes full responsibility for safe and compliant use.
Additional information
| CAS | 40077-57-4 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 125672 |
| Molecular Weight | 383.49 g/mol |
| Amino Acid Sequence | Lys-Pro-Val |
| PubChem Link | |
| Product Note | For laboratory use only. Not for human or veterinary use. Proper handling and storage (-20°C) are required to maintain stability. Ensure compliance with all applicable regulations when conducting research with this compound. Peptides will arrive in a lyophilized (powder) form for maximum stability. |