What is VIP (Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide)?
VIP is a high-purity synthetic peptide, a 28-amino acid neuropeptide belonging to the glucagon/secretin superfamily, designed exclusively for laboratory research. This peptide acts as a potent agonist of VIP receptors (VPAC1 and VPAC2), making it a valuable tool for investigating neuroendocrine regulation, anti-inflammatory pathways, and tissue repair mechanisms. Supplied as a lyophilized powder for reconstitution, VIP provides researchers with a precise compound to study its effects on immune modulation, metabolic homeostasis, and muscle physiology in experimental models.
VIP (Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide) Structure
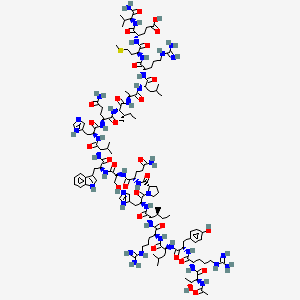
Molecular Formula
Molecular Weight
2675.1 g/mol
Computed by PubChem 2.2 (PubChem release 2025.04.14)
Research Applications:
VIP is extensively studied in preclinical research for its anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and tissue-protective properties in cellular and animal models. Investigations focus on its ability to suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6), which supports overall health by reducing chronic inflammation linked to metabolic disorders and obesity. Research also explores its role in promoting tissue repair and angiogenesis, which aids muscle recovery by enhancing blood flow and reducing oxidative stress following exercise or injury. Its potential to regulate energy metabolism and appetite through neuroendocrine signaling makes VIP a key compound for weight management and metabolic health studies.
Research Links:
-
Delgado, M., et al. (2004). “Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit inflammatory responses in vivo.” Journal of Immunology, 173(9), 5658-5668. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15494517/
-
Investigates VIP’s anti-inflammatory effects, relevant to muscle recovery and health.
-
-
Pozo, D., & Delgado, M. (2004). “Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) as a modulator of immune responses and inflammation.” Current Immunology Reviews, 1(1), 1-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15526193/
-
Examines VIP’s immunomodulatory role, supporting metabolic health research.
-
-
Said, S. I., & Mutt, V. (2008). “Vasoactive intestinal peptide: A versatile peptide with therapeutic potential in tissue repair.” Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1144, 239-246. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19076381/
-
Studies VIP’s role in tissue repair, with implications for muscle recovery.
-
-
Gomariz, R. P., et al. (2006). “VIP-PACAP system in immunity: New insights for multitarget therapy.” Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1070, 51-74. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16888150/
-
Explores VIP’s effects on immune function and inflammation, relevant to weight management.
-
-
Dickson, L., & Finlayson, K. (2009). “VPAC and PAC receptors: From ligands to function.” Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 121(3), 294-316. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19109992/
-
Discusses VIP’s receptor-mediated effects on metabolism and tissue repair.
-
Product Note:
For laboratory use only. Not for human or veterinary use. Proper handling and storage (-20°C) are required to maintain stability. Ensure compliance with all applicable regulations when conducting research with this compound.
Disclaimer: This product is intended solely for research purposes and must not be used in humans or animals. Purchaser assumes full responsibility for safe and compliant use.










